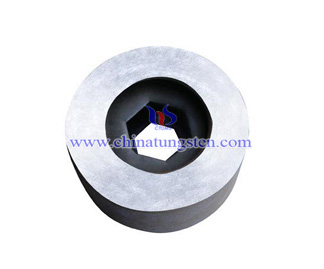
Tungsten Carbide Hexagonal Mould
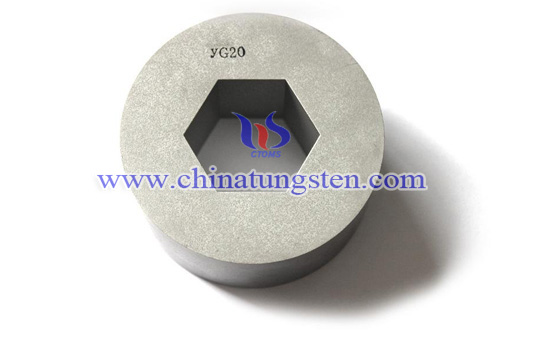
Introduction
Tungsten carbide hexagonal mould is one of the hard alloy tensile molds. The tungsten carbide hexagonal mould is ten times or even several times longer than the steel die. The tungsten carbide hexagonal mould has high hardness, high strength and corrosion resistance. High temperature resistance and small expansion coefficient, generally made of tungsten-cobalt hard alloy, the impurity content is extremely low, no explosive mold; and the service life is very long, the raw material adopts exclusive formula process, adding wear-resistant element material to make the die life Greatly improved; coupled with low processing cost, it is pressed and formed by imported presses, sintered by over-pressure sintering furnace, product hole type is positive, the dimensional tolerance is small, and the processing cost is lower.
Test Methods of Hardness
Tungsten carbide hexagonal mould test mainly uses a Rockwell hardness tester to test the HRA hardness value. The PHR series of portable Rockwell hardness testers are ideal for testing the hardness of cemented carbide. The weight accuracy of the instrument is the same as that of the desktop Rockwell hardness tester. It is very convenient to use and carry. Cemented carbide is a kind of metal. The hardness test can reflect the difference of mechanical properties of cemented carbide materials under different chemical compositions, microstructures and heat treatment conditions. Therefore, hardness test is widely used in the inspection and supervised heat treatment of cemented carbide properties. The correctness of the process and the study of new materials.
Methods
The tungsten carbide hexagonal mould is produced by mixing tungsten carbide and cobalt in a certain ratio, pressurizing into various shapes, and then semi-sintering. This sintering process is usually carried out in a vacuum furnace. It is placed in a vacuum furnace to complete the sintering, at which time the temperature is between about 1,300 and 1,500 degrees Celsius. Cemented carbide sintering is to press the powder into a billet, then heat it to a certain temperature (sintering temperature) in a sintering furnace, and keep it for a certain period of time (heating time), and then cool down to obtain a cemented carbide material with desired properties.